3-Omega Method
Investigation of the thermal conductivity of thin layers
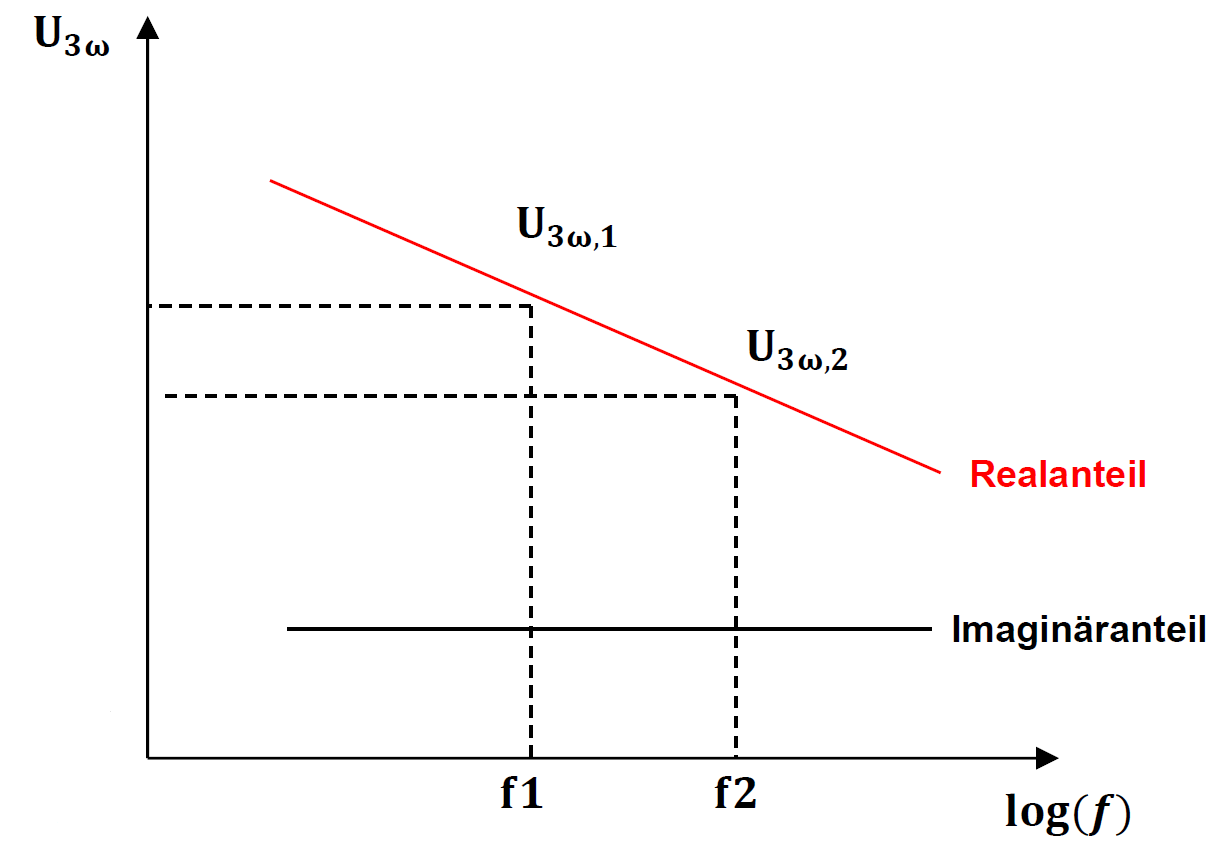
The 3-omega method is used to determine the thermal conductivity of thin layers. A linear heating source with the resistance R is applied to the sample to be examined. A periodic current is then applied to the applied heater, as a result of which the sample is also heated periodically. The resulting temperature oscillation can be measured. The thermal conductivity of the thin layer can now be determined from the frequency dependence of these oscillations.
The voltage measured on the heater consists of different frequencies. In addition to the fundamental frequency U (ω), a frequency U (3ω) also arises from the second harmonic, which is generated by the resistance oscillation. Due to the known temperature coefficient of the material, the thermal conductivity can be determined by mathematical transformation from the amplitude and its frequency-dependent slope.
Since the third harmonic wave is used for the determination, the method developed by David Cahill (1987) was also called the 3-omega method.