Simulation
The simulation of products, components or processes is an excellent way to supplement development processes. The main advantages are the simpler implementation of parameter variations, as well as the variation of boundary and environmental conditions. Time and cost savings can be achieved.
CFD-Simulation
With the help of a CFD simulation thermal and fluid dynamic processes
are pictured, resulting in temperature distributions and flow conditions. The results can be used, for example, to gain insights into pressure loss and thermal resistances. These results make a major contribution to development processes, even in the early stages of development.
FEM simulation
To picture mechanical loads
FEM simulations are carried out. An analysis of the stress and its effects on a system is possible through an FEM simulation. Through linking with thermal simulation, temperature fields can also be implemented as temperature loads. For example, there is a stress distribution or component deformation. A large area of application of the FEM simulation is the service life analysis. The FEM simulation offers advantages in the analysis of parameters and boundary conditions, which are difficult to investigate experimentally.
Optimization procedure
With the help of optimization processes, individual components - but also multidisciplinary systems - are efficiently improved with the help of algorithms.
For example, a large number of influencing parameters of heat sinks through which flow occurs, such as temperature, pressure loss, exchange surface and heat transfer (degree of turbulence), can be developed and improved according to defined requirements. Resource-intensive evaluations (e.g. complex CFD simulations) are dispensed with, which is associated with a significant reduction in variants and a high level of time savings.
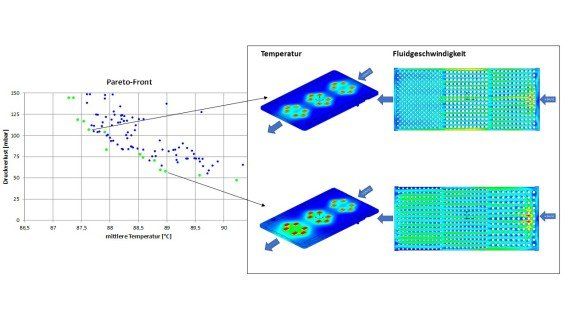
The simultaneous optimization of the parameters results in several local minima of the multidimensional optimization problem, which can be summarized in a so-called Pareto front (see figure). Here, heat sinks with the appropriate parameters can now be selected for different applications.
For example, a large number of influencing parameters of heat sinks through which flow occurs, such as temperature, pressure loss, exchange surface and heat transfer (degree of turbulence), can be developed and improved according to defined requirements. Resource-intensive evaluations (e.g. complex CFD simulations) are dispensed with, which is associated with a significant reduction in variants and a high level of time savings.
The simultaneous optimization of the parameters results in several local minima of the multidimensional optimization problem, which can be summarized in a so-called Pareto front (see figure). Here, heat sinks with the appropriate parameters can now be selected for different applications.